Orthotics and Shoe Inserts for Children with Intractable Epilepsy
 Families of children in early intervention programs and those who participate in physical therapy centers often have questions about the use of shoe inserts known as orthotics for their children. Although orthotics are mentioned in many books available to families and professionals, there are few magazine articles or newspaper stories that mention these commonly used shoe inserts that do make a difference to children with epilepsy that also have low muscle tone or an abnormal gait or teens who have pain or discomfort due to walking differently during early childhood and beyond.
Families of children in early intervention programs and those who participate in physical therapy centers often have questions about the use of shoe inserts known as orthotics for their children. Although orthotics are mentioned in many books available to families and professionals, there are few magazine articles or newspaper stories that mention these commonly used shoe inserts that do make a difference to children with epilepsy that also have low muscle tone or an abnormal gait or teens who have pain or discomfort due to walking differently during early childhood and beyond.
It is important to find shoes half a size larger than usual so that orthotics fit inside, and to have children’s feet measured regularly so that the orthotic and the shoe is the proper fit.
Mainstream children who do not develop a normal arch by the age of six are often referred for orthotics. Bracing may be recommended for children with low muscle tone (hypotonia). Too often, foot problems are not noticed or addressed in children with disabilities or their mainstream peers as early as should be done.
There are a variety of devices available, including orthotic braces, that require the expertise of a compassionate therapist or licensed professional to adjust and monitor over time. Custom orthotics or braces are available from many reputable sources, including hospital and university clinics, orthotics and prosthetics programs, physical therapists at early intervention centers, orthopedists and podiatrists.
Children and teens with disabilities are not the sole users of orthotics – they are also recommended for athletes in various sports to avoid injuries or help them heal afterward.
Early use of orthotics in children with an abnormal gait and excessive pronation or supination (see definitions below) may prevent painful changes that occur in bones, tendons, and muscles over time and cause permanent pain in the feet, legs and hips.
What is Supination?
 Supination is the opposite of pronation and refers to the outward roll of the foot during normal motion. A natural amount of supination occurs during the push-off phase of the running gait as the heel lifts off the ground and the forefoot and toes are used to propel the body forward. However, excessive supination (outward rolling) places a large strain on the muscles and tendons that stabilize the ankle, and can lead to the ankle rolling completely over, resulting in an ankle sprain or total ligament rupture.
Supination is the opposite of pronation and refers to the outward roll of the foot during normal motion. A natural amount of supination occurs during the push-off phase of the running gait as the heel lifts off the ground and the forefoot and toes are used to propel the body forward. However, excessive supination (outward rolling) places a large strain on the muscles and tendons that stabilize the ankle, and can lead to the ankle rolling completely over, resulting in an ankle sprain or total ligament rupture.
What is Pronation?
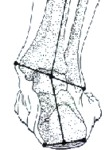
Pronation refers to the inward roll of the foot during normal motion and occurs as the outer edge of the heel strikes the ground and the foot rolls inward and flattens out. A moderate amount of pronation is required for the foot to function properly, however damage and injury can occur during excessive pronation. When excessive pronation does occur